You Don’t Need To Overpay For Technology Stocks – Forbes

businessman in office pushing touchscreen button mutual funds
Getty
My sector ratings show that the Technology sector receives a premium valuation compared to the market. Due to the high risk that comes with this elevated valuation, some investors might believe that diversifying their exposure through a Technology mutual fund is the best option. However, if the mutual fund chooses poor stocks and charges high fees, the results could be worse than picking your own stocks. Utilizing my Predictive Risk/Reward Fund rating methodology, I have identified a Technology fund that charges investors above average fees for overvalued stocks.
Despite its high Morningstar and Zacks rating, AllianzGI Technology Fund (RAGTX) is a mutual fund investors should avoid. RAGTX is in the Danger Zone.
Backwards Looking Research Overrates this Fund
Per Figure 1, RAGTX receives a 4-Star rating from Morningstar and a “Buy” rating from Zacks. When viewed through my Predictive Risk/Reward Fund Rating methodology, all share classes earn a very unattractive rating.
Figure 1: AllianzGI Technology Fund Ratings
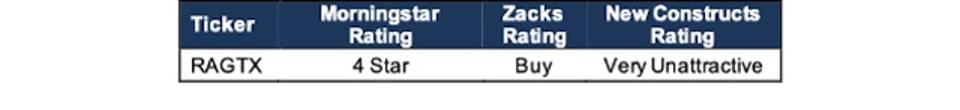
RAGTX Morningstar Zacks Vs. New Constructs Rating
New Constructs, LLC
RAGTX allocates significant capital to micro-bubble stocks – like Amazon (AMZN) – that make its past performance look good but pose elevated risk going forward. Investors that rely on past performance won’t understand the true risk of investing in this fund.
Holdings Research Reveals a Low-Quality Portfolio
The only justification for a mutual fund to charge higher fees than its ETF benchmark is “active” management that leads to out-performance. A fund is most likely to outperform if it has higher quality holdings than its benchmark. To assess holdings quality, I leverage my firm’s Robo-Analyst technology[1] to drill down and analyze the individual stocks in every fund under coverage.
Figure 2: RAGTX Allocates Capital to Lower-Quality Holdings
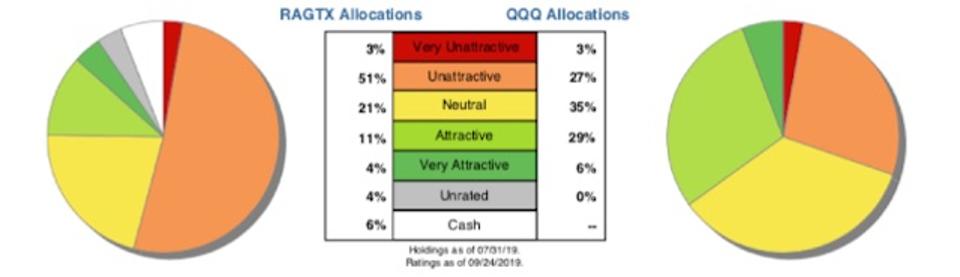
RAGTX vs. QQQ Allocation Ratings
New Constructs, LLC
Per Figure 2, AllianzGI Technology Fund’s asset allocation poses greater downside risk and holds less upside potential than its benchmark, the Invesco QQQ Trust (QQQ).
RAGTX allocates only 15% of its portfolio to attractive-or-better rated stocks compared to 35% for QQQ. On the flip side, RAGTX’s exposure to unattractive-or-worse rated stocks is much higher, at 54%, than QQQ, at 30%. See Figure 3.
Figure 3: RAGTX vs. QQQ – Attractive & Unattractive Asset Allocation
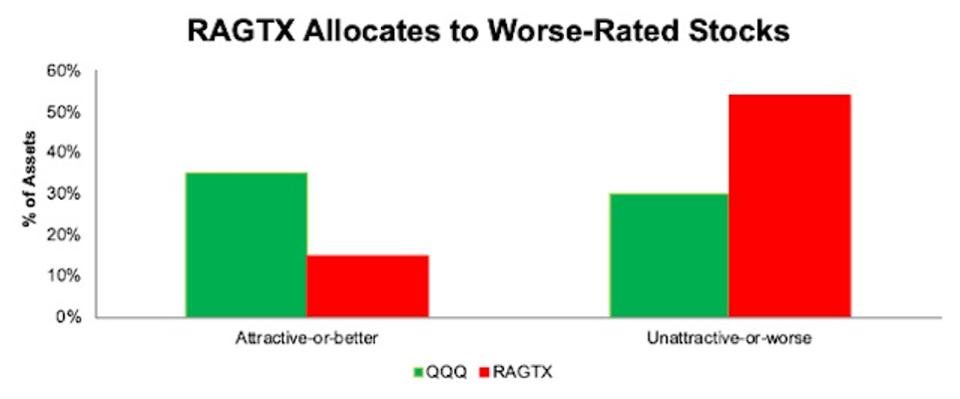
RAGTX vs. QQQ Attractive Vs. Unattractive Stocks
New Constructs, LLC
Six of the mutual fund’s top 10 holdings receive an unattractive-or-worse rating. These six stocks make up 23% of its portfolio.
Given the unfavorable allocation of very attractive vs. very unattractive stocks relative to the benchmark, RAGTX appears poorly positioned to generate the outperformance required to justify its fees.
Poor Stock Selection Process
The managers of RAGTX note their investment process has three key differentiators:
- The fund aims to identify significant secular growth trends ahead of the crowd and invest in companies that have good potential to become market leaders
- The fund invests in domestic and foreign technology stocks that demonstrate outstanding business models across many different market caps, valuations, and industries
- AllianzGI’s analyst conduct fundamental research, supplemented by their “Grassroots Research” to leverage an information advantage
However, these differentiators do not lead to a higher-quality portfolio than either its benchmark or the market (S&P 500) as a whole. The first differentiating factor, identifying major growth trends “before the crowd”, is a great strategy in theory, but less achievable in practice.
Four of its top 10 holdings, Microsoft (MSFT), Facebook (FB), Amazon.com (AMZN), and Mastercard (MA) have a market cap above $275 billion and many would consider them industry leaders. Microsoft and Amazon are two of only three companies to ever achieve a trillion dollar market cap. I don’t think anyone would argue these firms haven’t been “recognized by the crowd”. As of 8/31/19, these four companies made up over 22% of RAGTX’s portfolio.
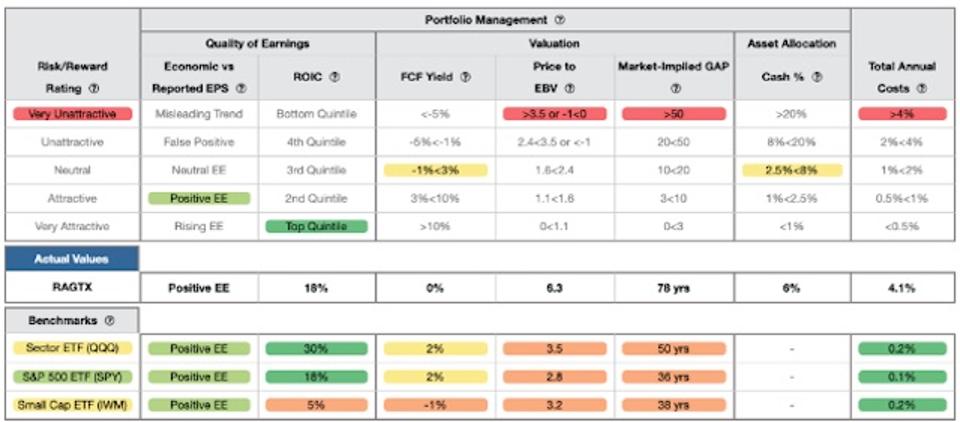
In addition, RAGTX’s “information advantage” has not resulted in its manager’s finding more profitable or less expensive businesses than the benchmark. Figure 4 contains my detailed rating for RAGTX, which includes each of the criteria I use to rate all funds under coverage. These criteria are the same for my Stock Rating Methodology because the performance of a fund’s holdings equals the performance of a fund after fees.
Figure 4: AllianzGI Technology Fund Rating Breakdown
RAGTX Rating Breakdown
New Constructs, LLC
As Figure 4 shows, RAGTX’s holdings are inferior to QQQ in all four of the five criteria that make up my holdings analysis. Specifically:
- RAGTX’s return on invested capital (ROIC) is 18%, which is nearly half the 30% earned by QQQ and equal to the S&P 500 (SPY).
- RAGTX’s free cash flow yield of 0% is less than QQQ and SPY at 2%.
- The price to economic book value (PEBV) ratio for RAGTX is 6.3, which is significantly greater than the 3.5 for QQQ holdings and the 2.8 of SPY holdings.
- My discounted cash flow analysis reveals an average market implied growth appreciation period (GAP) of 78 years for RAGTX’s holdings compared to 50 years for QQQ and 36 years for SPY.
The stocks held by RAGTX generate inferior cash flows compared to QQQ, yet the market expects stocks held by RAGTX to grow profits by nearly double that of QQQ stocks. Lower historical profits and higher expectations for future profits do not make a good combination.
How Using the Wrong Metrics Leads to Bad Stocks
By focusing on the Technology sector, and subsequently allocating to some of the most overvalued stocks in the sector, RAGTX’s holdings include many previous Danger Zone picks, such as Yelp (YELP), GoDaddy (GDDY), Twitter (TWTR), ServiceNow (NOW), Square (SQ), Zendesk (ZEN), Snap (SNAP), Proofpoint (PFPT), Splunk (SPLK), Dropbox (DBX), Netflix (NFLX), and more.
Shopify (SHOP) is one of the holdings that illustrates the type of low-quality stocks in RAGTX’s portfolio. Since 2015, SHOP’s economic losses have increased more than eight times over, despite impressive revenue growth.
SHOP’s revenue has grown 74% compounded annually since 2015 and TTM revenue is up 52% over the prior TTM period. Meanwhile economic earnings, the true cash flows of the business, have fallen from -$22 million in 2015 to -$188 million TTM.
Figure 5: SHOP’s Economic Earnings Fall Despite Revenue Growth
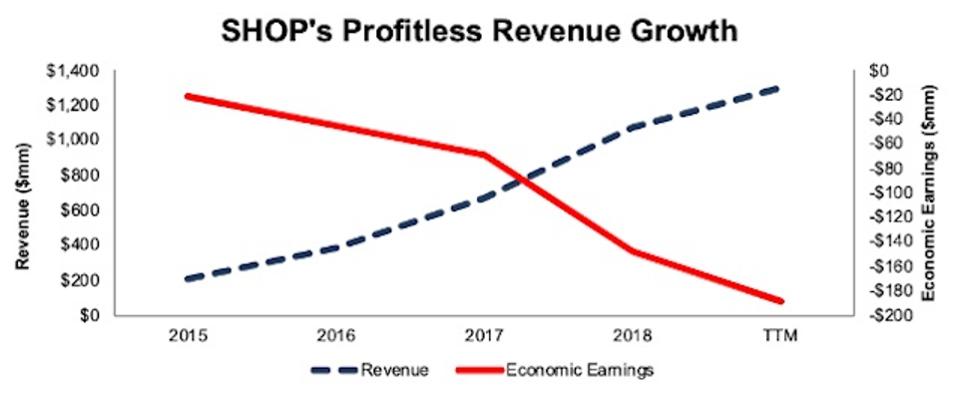
SHOP Revenue Vs. Economic Earnings
New Constructs, LLC
Economic earnings account for non-operating expenses and income, such as the $29 million (3% of 2018 revenue) in interest income reported on SHOP’s 2018 income statement. Only by adjusting for these non-operating items can one calculate the true operating profits of the business.
Economic earnings also account for changes to the balance sheet, and include items hidden (not for long) off the balance sheet, such as $407 million (19% of reported net assets) in off-balance sheet operating leases.
By adding these leases back to invested capital, I hold SHOP accountable for all capital invested in the business. These adjustments, when combined with a rising weighted average cost of capital (11.4% TTM, up from 10.7% in 2015), increase the capital charge and decrease economic earnings.
Despite the deterioration in the true profits of the company, shares have increased more than tenfold since 2015 and are drastically overvalued – even by tech company standards.
Overvaluation Means All Good News Is More Than Priced In
Even by traditional valuation metrics, SHOP is significantly overvalued. Its price-to-sales (P/S) ratio of 27 is over six times the P/S ratio of the entire Technology sector and over 12 times the entire market. I use my reverse DCF model to quantify the growth in cash flows SHOP must achieve to justify its valuation.
To determine a reasonable expectation for Shopify’s future margins, I analyzed some of its publicly traded competitors: Adobe Systems (ADBE), which owns e-commerce platform Magento, GoDaddy (GDDY), which offers e-commerce tools through its site builder, Square (SQ) acquired website builder Weebly in 2018, and Wix (WIX), which offers e-commerce solutions through its website builder as well. See Figure 6 for more details.
Figure 6: Margin Comparison – Shopify vs. Competitors
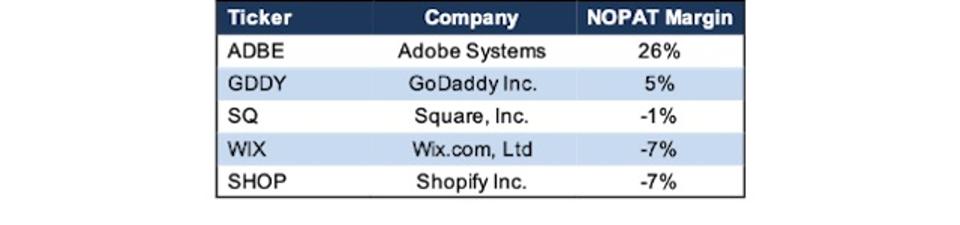
SHOP Margin Comparison Vs. Competitors
New Constructs, LLC
Adobe’s margins are significantly higher than other competitors. Even at 5%, GoDaddy’s margins are much higher than Shopify’s -7%. These benchmarks help illustrate just how high the expectations baked into SHOP are.
To justify its current price of $306/share, SHOP must immediately achieve 26% NOPAT margins (equal to Adobe and up from its current -7%) and also grow revenue by 33% compounded annually for the next 11 years. See the math behind this dynamic DCF scenario.
In this scenario, SHOP would be generating nearly $32 billion in revenue, which is more than ADBE, GDDY, SQ, and WIX’s 2018 revenue combined. This scenario seems even more optimistic given that SHOP hasn’t achieved positive NOPAT margins since its IPO. Plus, its margin is trending down since 2017.
Even if I assume SHOP can achieve 10% NOPAT margins, double GDDY, which has its own issues, and still grow revenue by 34% compounded annually for the next decade, the stock is worth only $94/share today – a 69% downside. See the math behind this dynamic DCF scenario.
Excessive Fees Make Outperformance Even More Difficult
At 4.11%, RAGTX’s total annual costs (TAC) are higher than 98% of the 145 Technology sector mutual funds under coverage. For comparison, the average TAC of all Technology mutual funds under coverage is 1.98%, the weighted average is 1.62%, and the benchmark ETF (QQQ) has total annual costs of 0.22%.
My TAC metric accounts for more than just expense ratios. I consider the impact of front-end loads, back-end loads, redemption fees, and transaction costs. For example, RAGTX’s front-end load adds 2.09% to its total annual costs and its annual turnover ratio of 109% adds 0.24% to its total annual costs – neither of which are captured by the expense ratio. Figure 7 shows my breakdown of RAGTX’s total annual costs, which is available for all of the 7,500+ mutual funds under coverage.
Figure 7: AllianzGI Technology Fund Total Annual Costs Breakdown
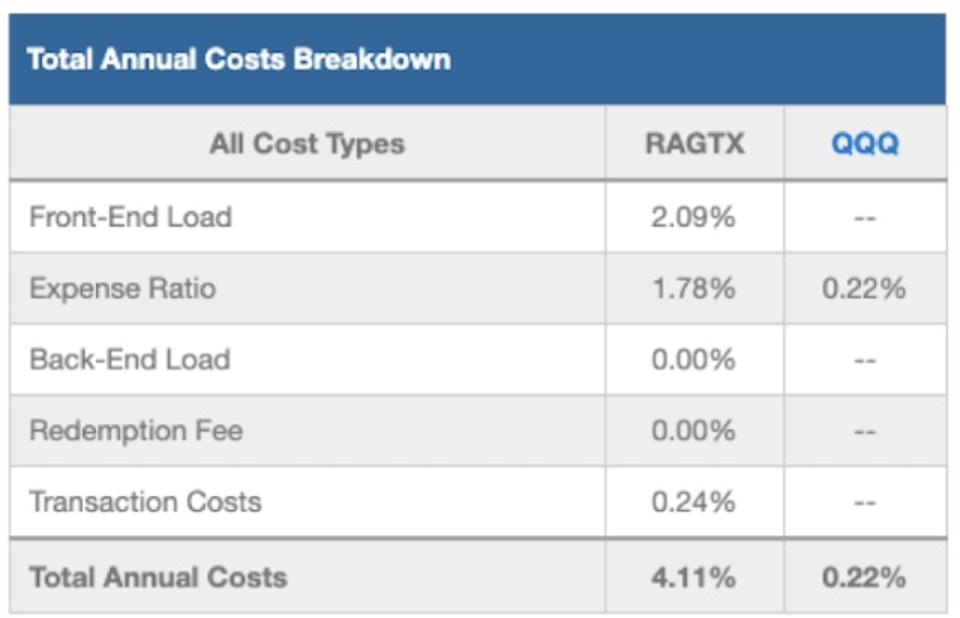
RAGTX Total Annual Costs Breakdown
New Constructs, LLC
To justify its higher fees, RAGTX much outperform its benchmark by 3.88% annually over three years or 2.39% annually over 10 years.
RAGTX’s Performance Can’t Justify Its Fees
When I take into account its load, which adds 2.09% to its total annual costs, I see that RAGTX has underperformed in recent years and failed to justify its fees.
RAGTX’s 1-year quarter-end average annual total return underperformed QQQ by over 350 basis points. Its 5-year quarter-end average annual total return outperformed by just 18 basis points, which is not enough to justify its fees, as noted above. Finally, its 10-year quarter-end average annual total return underperformed QQQ by 84 basis points.
Given that 54% of assets are allocated to stocks with Unattractive-or-worse ratings, RAGTX looks likely to underperform moving forward.
The Importance of Holdings-Based Fund Analysis
Smart fund (or ETF) investing means analyzing the holdings of each mutual fund. Failure to do so is a failure to perform proper due diligence. Simply buying a mutual fund or ETF based on past performance does not necessarily lead to outperformance. Only through holdings-based analysis can one determine if a fund’s methodology leads managers to pick high-quality or low-quality stocks.
Highly Rated Technology Mutual Funds
The following Technology mutual funds earn an attractive-or-better rating, have more than $100 million in assets under management, and have lower TAC than RAGTX.
- Oak Associates Red Oak Technology Select Fund (ROGSX) – very attractive – 1.06% TAC
- Fidelity Select Computers Portfolio (FDCPX) – very attractive – 1.02% TAC
Disclosure: David Trainer, Kyle Guske II, and Sam McBride receive no compensation to write about any specific stock, sector, style, or theme.
[1] Harvard Business School features the powerful impact of my firm’s research automation technology in the case study New Constructs: Disrupting Fundamental Analysis with Robo-Analysts.
[2] This paper compares my firm’s analytics on a mega cap company to other major providers.