What is astrophysics? | Space – EarthSky
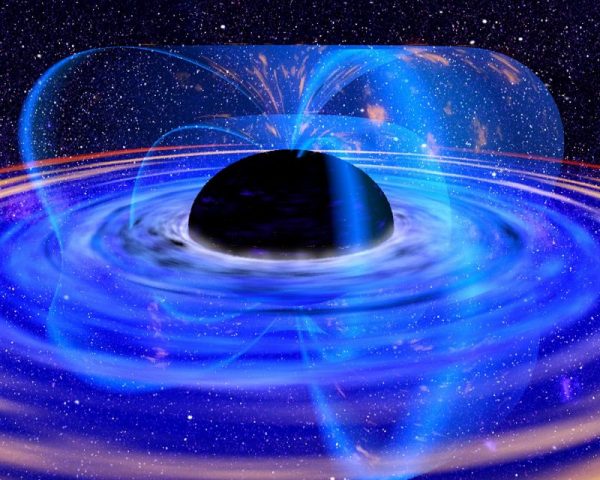

Artist’s concept of a black hole. Astronomers use telescopes, both on Earth and in space, to gather radiation from space objects. Astrophysicists wield the laws of physics and physical theories to interpret that radiation. Ultimately, from the observations of astronomers, the minds and labor of astrophysicists – and the imaginations of space artists – we have images like this one. Image via Dana Berry/ NASA/ Wikimedia Commons.
Astrophysics is the science of physical processes in the cosmos. It uses data gathered by astronomers using telescopes on Earth and in space – combined with the laws and theories of physics – in order to interpret the universe around us. If astronomy asks what and where, astrophysics asks how and why. A sister science – planetary science – studies the planets in our solar system and distant solar systems in our Milky Way galaxy. Another sister science – cosmology – studies external galaxies and voids, and the large-scale structure and history of the universe.
For example, an astronomer might spend nights at the telescope gathering data on a star. Putting on his or her astrophysicist hat – and depending on which instruments were used in conjunction with the telescope (photometers or spectrometers, for example) – that scientist would then turn to the laws of physics to understand how that star produces its energy, whether it has a companion (or perhaps planets, or perhaps an encircling disk), and how the star moves through space.
Galactic astrophysicists would then ask how that star fits with what’s known about our Milky Way galaxy.
Cosmologists would then ask how the knowledge of the stars fits with that of the universe as a whole.
And by the way all of these labels – astronomer, astrophysicist, cosmologist, for example – might describe a single person whose job is to study and understand the universe.
Plus this description is just a very, very simplistic view of what astronomers/astrophysicists/cosmologists actually do. They might, for example, bring many other sciences into their studies: chemistry, geology, biology and more. They’ll bring all of this knowledge into focus using a powerful and complex arsenal of theories, instruments and computational power that would have been unthinkable just a few decades ago. All of the tools of astronomy, all its various devices, data, theories and pathways of study, are seeking to answer humanity’s biggest questions. How did our universe get here? What’s its history? Where did we come from? Are there others like us, elsewhere in the cosmos?

Ultimately, astrophysics is a tool that helps humanity understand its place in the cosmos.
The history of astrophysics really begins in Europe with the Renaissance, when astronomy threw off the shackles of eons-old myths and became a true science. In Florence, in 1610, Galileo Galilei became one of the first to turn the telescope to the sky, revealing a universe at odds with the restrictive teachings of the Church. By 1633, this dangerous contradiction saw Galileo tried by the Roman Inquisition and confined to house arrest for the rest of his life until his death in 1642.

A painting by Giuseppe Bertini (1858), depicting Galileo (standing) showing the Doge or Duke of Venice (seated) how to use a telescope. Galileo is remembered as one of the first great observational astronomers. Image via Wikimedia Commons.
In England in 1665, Isaac Newton, having fled Cambridge University to escape the Great Plague, settled back in the town of his birth, the rural community of Woolsthorpe, Lincolnshire. Over the next several years, he developed calculus and revolutionary ideas about light. In 1687, he published his Law of Universal Gravitation, stating that every particle attracts every other particle in the universe with a force that is directly proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them. For the first time, scientists could calculate the force of attraction between objects in space. This was a giant step forward in scientists’ ability to understand the heavens.

Isaac Newton (1642-1726). He famously said in the year 1675: “If I have seen further it is by standing on the shoulders of Giants.” Image via teachertech.rice.edu.
It can therefore be argued that Newton was the first astrophysicist, using the mathematical and physical tools he himself developed to ask questions about the nature of physical processes in the cosmos.
But the most important realization to emerge from Newton’s era was simply that the universe is governed by physical processes. Given the right tools, these processes can be understood by humans. No longer did the universe obey the whims of mystical and unfathomable powers: what was out there was just physics.
In the 20th century, Albert Einstein initiated a new revolution in our understanding of gravity with his general theory of relativity.
Now it’s estimated that what we know about the cosmos is doubling every 10 years.
A large part of that knowledge comes from the continued contribution of astrophysicists to our understanding of the laws of nature at work in the universe.
The 2020 lunar calendars are nearly sold out! Order yours before they’re gone. Makes a great gift!
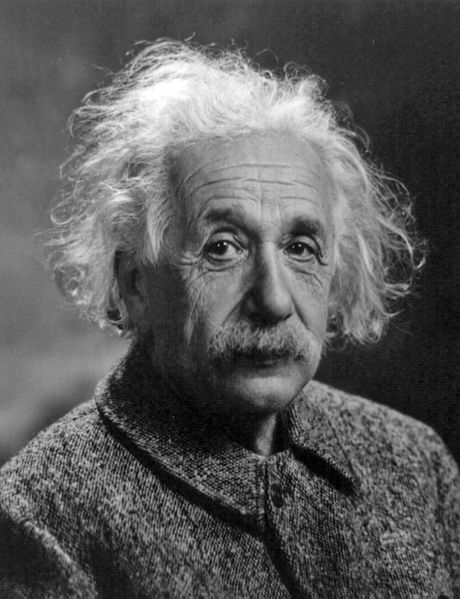

Einstein in 1947, at the age of 68. His special and general theories of relativity altered the way astrophysicists think about space, matter and time.
Bottom line: Observational astronomy and astrophysics work together to further our understanding of the cosmos. Astrophysicists apply the laws of physics and physical theories to interpret the light gathered by observational astronomers.