Voyager: What’s next for NASA’s interstellar probes? – Astronomy Magazine
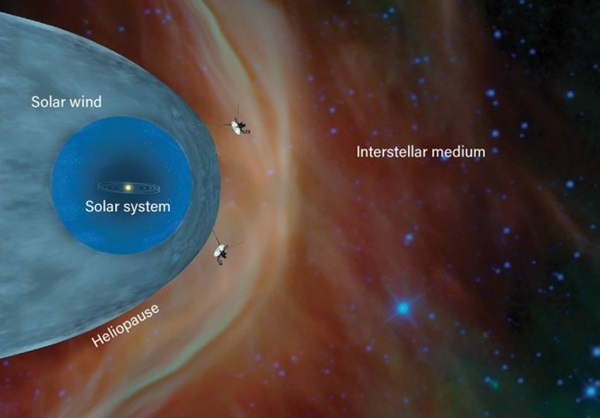
Only the Voyager probes have passed the heliopause, leaving the sun’s influence. New probes may one day study the interstellar medium lying beyond.
NASA-JPL/Caltech
What is the Voyager Mission Studying?
Back in 2012, Voyager 1 became the first spacecraft to reach interstellar space. There are no road signs letting NASA know that the craft broke the barrier. Instead, they determined it thanks to measurable changes Voyager 1 detected when it hit a region called the heliopause.
Our Sun produces an intense stream of particles, dubbed the solar wind, that flows outward in all directions and creates a magnetic field that shields the planets from interstellar particles. The powerful wind carves a huge cavity in the interstellar medium (the region between stars) that encapsulates all the planets. This protective bubble is called the heliosphere, and the heliopause is its outer boundary — where our Sun’s influence is finally overpowered by distant activity like erupting supernovas.
Scientists were surprised when Voyager 1 measured the magnetic field just inside and just outside of the heliopause, finding no significant changes in its overall direction. Then, when Voyager 2 reached this same boundary of interstellar space in 2018, it found similar results.
But Voyager 2 offered up another surprise when NASA scientists released its first results from beyond the heliopause. They had originally expected that particles from our sun would not “leak out” of the heliosphere into interstellar space. And Voyager 1 saw no such leakage. But Voyager 2 found the opposite. It recorded a small trickle of solar particles streaming through the heliopause.
In recent years, the twin probes also have discovered that the solar wind moves more slowly at our solar system’s edge than expected. All said, by studying data from the two probes, astronomers have been able to compare, contrast and confirm results about the boundary that separates our solar system from interstellar space.