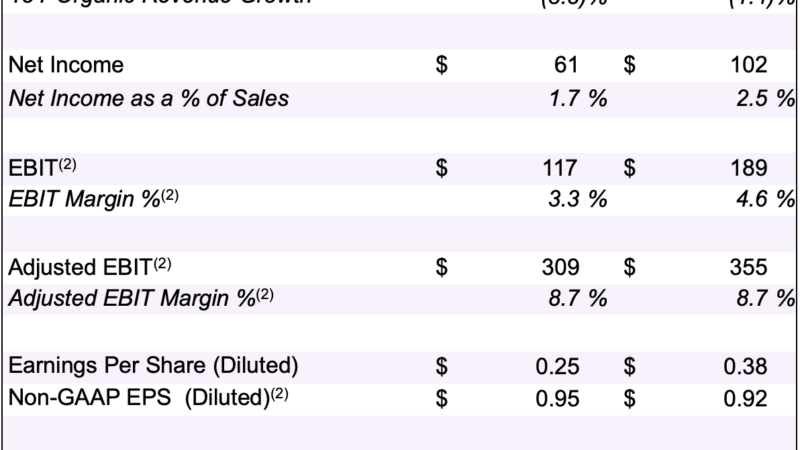
The 7 Biggest Technology Trends To Disrupt Banking & Financial Services In 2020 – Forbes
Even though banking and financial services have been slower than other industries to adopt the latest technology into their operations, financial organizations are trying to catch up by incorporating artificial intelligence, blockchain, and other technology to benefit their customers, remain competitive and improve business results. Here are the 7 biggest technology trends that will disrupt banking and financial services in 2020.

The 7 Biggest Technology Trends To Disrupt Banking & Financial Services In 2020
Adobe Stock
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
Although banking and financial services tend to be slower to adopt new technologies, a PricewaterhouseCooper study confirms the majority of financial services decision-makers are investing in artificial intelligence (AI)—52 percent of executives confirmed they are making “substantial” investments in AI while 72 percent believe it will be a business advantage. One thing that will likely make the rest believe in artificial intelligence’s potential for the industry are the cost savings that are expected to be $447 billion by 2023.
So, how do financial institutions use artificial intelligence? The most visible way the banking industry uses artificial intelligence (AI) is for customer service from chatbots and robots. Many of the largest financial institutions, such as Bank of America and JPMorgan Chase, use AI to streamline customer service. Another customer-facing way AI is deployed is to facilitate mobile banking that allows 24/7 access for consumers to conduct banking operations. AI is also instrumental in the way financial institutions enhance security and prevent and detect fraud. The technology helps financial institutions with risk management and lending decisions and is foundational in making other technology such as big data analytics, robotic process automation, and voice interfaces work.
Blockchain
Blockchain technology, first used in the cryptocurrency Bitcoin, is a distributed database that can keep track of transactions in a verifiable and permanent way. The Harvard Business Review predicts that blockchain will disrupt banks the way the internet disrupted media. Blockchains are transparent, highly secure, and are relatively cheap to operate. As more financial institutions realize how blockchain can improve security, save money, and improve customer satisfaction, more will adopt the technology.
Blockchain can support banking in several ways. Bitcoin showed how it can be used for payments, but it can also be transformative in the way our capital markets work by tokenizing traditional bonds, stocks, and other assets and putting them on public blockchains. Blockchains would remove the gatekeepers and third parties in the loans and credit system while also making it more secure to borrow money and lowering interest rates. Blockchain could also eliminate manual data reconciliation for bank ledgers. The way information and money are exchanged today will be altered by smart contracts that operate from blockchain technology.
Big Data
One of the ways to determine a technology’s influence on an industry is to look at how an industry is investing in it. The banking sector is currently one of the top investors by industry in big data and business analytics solutions according to the IDC Semiannual Big Data and Analytics Spending Guide. The amount of data generated by the financial industry—credit card transactions, ATM withdrawals, credit scores—is mind-boggling. And being able to put that data to use to make business decisions and process it effectively to glean actionable insights will be critical to staying competitive in the future.
Financial institutions can use big data to learn more about customers and be able to make business decisions in real-time including learning about a customer’s spending habits, sales management such as segmenting customers to optimize marketing as well as product cross-selling, fraud management, risk assessment, and reporting, and customer feedback analysis. Not only does big data analysis help identify market trends, but it also helps financial institutions streamline internal processes and reduce risk.
Robotic Process Automation (RPA)
Since robotic process automation can save labor, operational costs, and minimize errors, many financial institutions are starting to leverage this technology to create the best possible user experience for customers and to remain competitive. In RPA, software is programmed to enable robots and virtual assistants to complete repetitive and labor-intensive tasks correctly and quickly without human intervention.
RPA, through customer service chatbots helps banks deal with the low-priority queries from customers such as account and payment questions to free up human customer agents to deal with the high-priority concerns. In insurance companies, RPA is used to automate parts of the claims-handling processes. Another way RPA influences financial institutions is to help ensure compliance in the highly regulated industry. Today, thanks to RPA, customers can get a decision on their credit card application within a few hours but sometimes almost immediately after they submit the information. It’s also optimizing mortgage processing.
Cloud Computing
Cloud computing is technology for storing data and delivering computing services, including servers, databases, networking, software, analytics and more over the internet. When an individual or a business wants to use the cloud, they will pay a cloud provider based on usage with pay-as-you-go pricing.
Cloud computing makes 24/7 customer service from anywhere possible. In addition, cloud computing enhances the agility of financial institutions and makes scaling up services easier and quicker. Since they only pay for services they use, cloud computing can help financial institutions control costs. Cloud computing also enables secure online payments, digital wallets, and online transfers.
Voice Interfaces
Chatbot solutions, enabled by sophisticated artificial intelligence, are being deployed by financial institutions to reduce costs and meet customers’ expectations regarding quick response and effective issue resolution. Traditional forms of two-way communication such as email, phone, and text can be replaced with a chatbot. By 2020, chatbots are expected to handle no less than 85 percent of customer service interactions, according to Gartner.
Chatbots offer a nearly instant conversational experience that that can be personalized, so customers get premium service expeditiously. Bank of America, Capital One and Wells Fargo have used chatbots for years for simple account queries, but today’s advanced chatbots could even offer financial advice. Bots are also able to provide centralized financial management over the multiple channels that customers interact with their financial institution, correcting what had in the past felt disjointed. This technology continues to improve and will empower customers to connect with their bank on their terms.
Cyber Security and Resilience
In an industry dealing with sensitive personal and financial information, and that’s an attractive target of cybercriminals, security is paramount for financial institutions. It would be a good idea for financial institutions to assume there will be a security breach and plan for how to minimize the damage, because preventing all cyberattacks is nearly impossible due to the diverse ways consumers interact with their money and the numerous vulnerabilities that exist regardless of how much time and energy is put forth to prevent cyberattacks. From mobile apps and web portals to third-party networks and even susceptibilities introduced by employees and customers themselves, safety is never ensured even if you can thwart an attack periodically.
Financial institutions must do more than invest in technical measures to protect against cyberattacks. They must share knowledge and best practices with each other, work with governments to ensure cybersecurity is prioritized, be proactive about educating employees regarding their cybersecurity responsibilities and the importance of following protocols, and reaching out to the public to help them understand the situation and their role in keeping their personal data safe.