Space discovery: Astronomers detect ‘holy grail’ of oxygen in the universe’s oldest galaxy – Express.co.uk
ASTRONOMERS observing the depths of space with powerful telescopes have found traces of oxygen in galaxy born shortly after the universe came into existence.
The groundbreaking discovery proves astronomers’ ability to study distant galaxies without having to venture into space. In a press release, researchers at Leiden University in the Netherlands called the discovery a “holy grail” of astronomy.
Researchers at Leiden University and the University of Texas, Austin, in the US, believe the find will help astronomers map out the universe.
The discovery was achieved by observing “the fingerprint of oxygen” in the distant galaxy G09.83808.
Astronomers believe G09.83808 took shape around one billion years after the Big Bang, making it one of the oldest clusters of stars in the universe.
For comparison, the universe is estimated to be about 13.8 billion years old, making G09.83808 about 12.8 billion-years-old.
READ MORE: Millions of ‘nuclear bomb-like’ asteroids threaten Earth

Space discovery: Astronomers have found traces of oxygen in a distant and ancient galaxy (Image: GETTY)

Space discovery: The galaxy formed one billion years after the Big Bang (Image: GETTY)
READ MORE
-

Moon landing: How Neil Armstrong and Buzz Aldrin ‘ignored NASA’
Until now, it was thought impossible to make such discoveries with ground-based observatories.
To detect the oxygen fingerprint, astronomers had to aim their telescope at the galaxy for approximately two hours.
The telescope they used was the Atacama Pathfinder Experiment or APEX in Chile.
Mounted about 16,614ft (5,064m) above sea level, the powerful instrument sits in the desolate Atacama desert.
Earth-based telescopes like APEX are typically not equipped to make such discoveries in deep space.
But a specially built instrument in the Netherlands helped the astronomers detect an atomic oxygen spectral line.
Spectral lines are like atomic fingerprints that can identify atoms or molecules present within a burning star, galaxy or nebula.
The new atomic oxygen spectral line has been seen as a holy grail for 20 years
Spectral lines appear as black lines cutting across the spectrum of visible light from a source.
Astronomers can isolate the light and spilt it through a prism, like a rainbow, to detect individual spectral lines and their source material.
Because different atoms, molecules and ions boast different energy levels, they have different absorption lines when absorbing photons of light.
DON’T MISS
NASA almost failed to detect ANOTHER asteroid [INSIGHT]
Asteroid shock: We’d have little time to react if asteroid came [ANALYSIS]
NASA’s most terrifying photos of the Australian inferno [PICTURES]

Space discovery: Spectral lines can reveal the composition of stars and galaxies (Image: SWINBURNE UNIVERSITY)
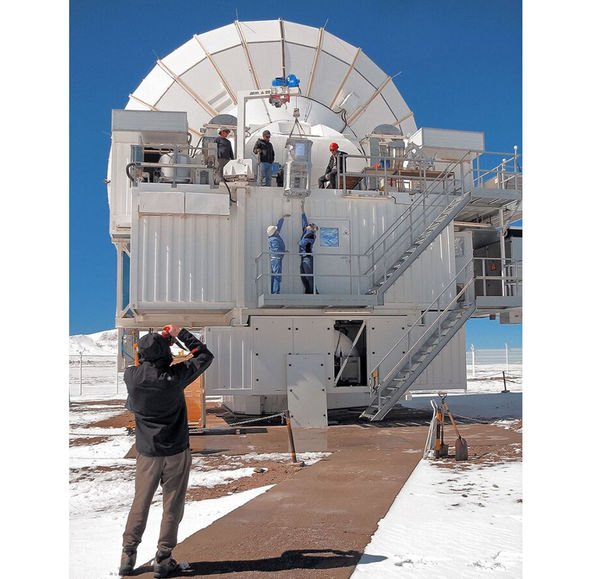

Space discovery: The APEX telescope sits in the Atacama desert in Chile (Image: ESO/Onsala Space Observatory/A. Ermakov)
READ MORE
-

NASA breakthrough: ‘Goldilocks Stars’ boost hopes of finding aliens
According to the University of Swinburne in Australia, the spectral lines of a specific element always occur on the same wavelength.
As a result, astronomers were able to detect oxygen spectral lines in the light hitting Earth from G09.83808.
Leiden University said in a statement: “The new atomic oxygen spectral line has been seen as a holy grail for 20 years, but the galaxies really have to be far away.
“For not too distant galaxies, the light from the oxygen line does not penetrate through the Earth’s atmosphere.
“But, even when galaxies are very far away, you need very good telescopes in a high, dry place.”
Technology has, however, advanced well enough to open up new avenues of discovery to astronomers.
The astronomers are now preparing to publish their findings in the journal Astrophysical Journal Letters.
Their study has for now been pre-published on the Cornell University .
In their study, the researches wrote: “Thanks to its brightness, ground-based studies of the [O I] 63-µm line will open a new window into the physics of star-forming neutral ISM in the first billion years of the cosmic history.’