Monster ‘Loner’ Star Causes Scientists to Rethink Supernova Explosions – Space.com
A massive supernova spotted in an isolated part of the universe has revealed a number of odd qualities, and just might be one of the most powerful explosions ever observed.
Observations of supernova, named SN 2016iet, have forced scientists to rethink how massive stars ended their lives in the early universe. It is the most massive star astronomers have ever seen die in a supernova explosion, officials with the Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics said in a statement.
The star, located in a distant dwarf galaxy about a billion light-years from Earth, was first spotted by the European Space Agency’s (ESA) Gaia satellite in November 2016. Following three years of observations, the team of scientists concluded that the supernova started off as a star 200 times the mass of the sun and formed in an isolated area around 54,000 light-years away from the center of its host dwarf galaxy (a light-year is the distance light travels in a year, roughly 6 trillion miles or 10 trillion kilometers).
Related: Supernova Photos: Great Images of Star Explosions
“When we first realized how thoroughly unusual SN 2016iet is, my reaction was, ‘Whoa – did something go horribly wrong with our data?'” Sebastian Gomez, Harvard University graduate student and lead author of the paper, said in the statement.
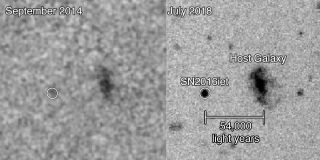
The supernova SN2016iet as first seen in September 2014 (left) and then again in July 2018. The latter observations revealed which revealed the host star’s 54,000 light-year distance from its galaxy.
(Image credit: Center for Astrophysics)
The star lost around 85% of its mass during its short-lived existence of only a few million years before it exploded, and the material it shed before its death collided with the debris from the explosion, which led to the supernova’s unusual qualities.
“Everything about this supernova looks different, its change in brightness with time, its spectrum, the galaxy it is located in, and even where it’s located within its galaxy,” Edo Berger, astronomy professor at Harvard University and co-author of the study, said in the statement. “We sometimes see supernovas that are unusual in one respect but otherwise are normal; this one is unique in every possible way.”
The supernova also had an unusually long duration, an odd chemical fingerprint and a lack of heavy metals in its environment — all qualities that have not been observed in any other supernova before it.
SN 2016iet marked the first observation of a pair-instability supernova that astronomers were able to observe. A pair-instability supernova occurs when the collapsing core of a dying star produces gamma-ray radiation that leads to the production of particle and antiparticle pairs, and those pairs cause a thermonuclear explosion that annihilates the star.
“The idea of pair-instability supernovas has been around for decades,” Berger said. “But finally having the first observational example that puts a dying star in the right regime of mass, with the right behavior, and in a metal-poor dwarf galaxy is an incredible step forward.”
The findings were published Aug. 15 in the Astrophysical Journal.
Follow Passant Rabie on Twitter @passantrabie. Follow us on Twitter @Spacedotcom and on Facebook.