Lasers usher in a new era of astronomy – University of Rochester
January 5, 2023
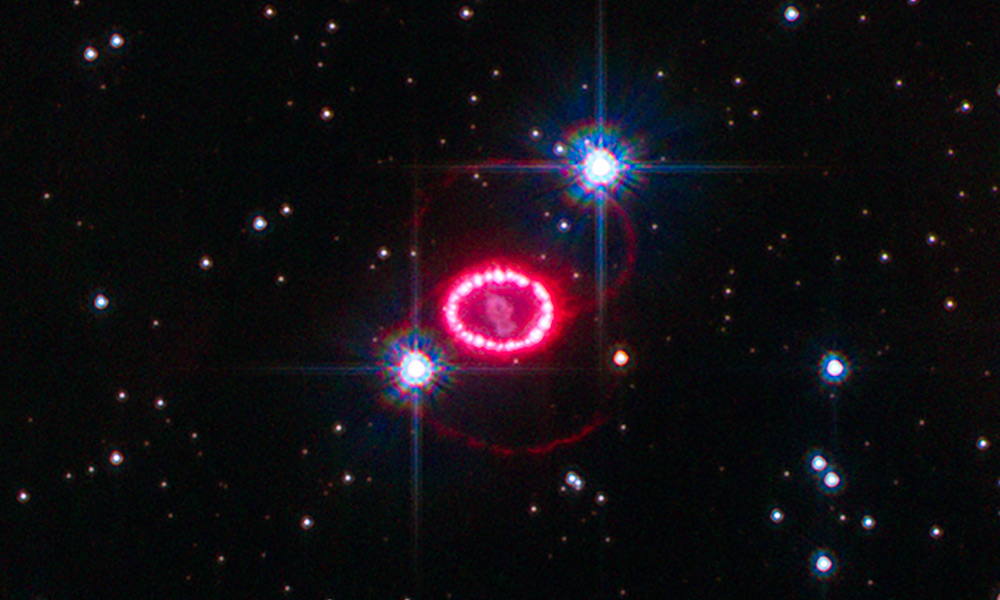 This 2010 NASA image from the Hubble Space Telescope shows the entire region around Supernova 1987A. Large lasers, such as the OMEGA laser at Rochester’s Laboratory for Laser Energetics, have allowed researchers “to explode mini supernovas in their labs,” writes University of Rochester astrophysicist Adam Frank in The Atlantic. (NASA Goddard photo)
This 2010 NASA image from the Hubble Space Telescope shows the entire region around Supernova 1987A. Large lasers, such as the OMEGA laser at Rochester’s Laboratory for Laser Energetics, have allowed researchers “to explode mini supernovas in their labs,” writes University of Rochester astrophysicist Adam Frank in The Atlantic. (NASA Goddard photo)Large-scale, laser-based experiments have recently revolutionized astrophysics, allowing scientists to recreate the cosmos in science labs.
In an article published in The Atlantic, Adam Frank, the Helen F. and Fred H. Gowen Professor of Physics and Astronomy at the University of Rochester, discusses what he calls this new era of astronomy. As he explains, a field called High Energy Density Laboratory Astrophysics (HEDLA) has emerged around lasers, which provide scientists an entirely new realm to better understand planetary conditions and other phenomena in the universe.
Large lasers, such as the OMEGA laser at Rochester’s Laboratory for Laser Energetics, have allowed researchers “to explode mini supernovas in their labs, reproduce environments around newborn stars, and even probe the hearts of massive and potentially habitable exoplanets,” Frank writes.
He attributes the emergence of large-scale, lab-based astrophysics to the decades-long quest for nuclear fusion. Last month, for instance, the Department of Energy announced that scientists had reached a fusion milestone when they achieved ignition—that is, more energy was released from the fusion reaction than was expended in generating it. To accomplish this feat, researchers used lasers to recreate conditions that exist at the core of the sun, where fusion reactions already occur.
“They focused the lasers on tiny pellets of hydrogen, mimicking the sun’s extraordinarily high temperatures and densities to squeeze the hydrogen nuclei into helium and kick off fusion reactions,” Frank writes. “The lasers used are factory-sized affairs that require enormous power to do their work. It was in the process of building these multistory light machines that scientists realized they were also incidentally building an unprecedented tool for studying the heavens.”
As for the future of HEDLA research, Frank says a “sweet spot” may be using laser-based experiments to assist in the search for distant worlds that could potentially harbor life.
“The universe is more in our hands than ever before,” he writes.
Read the full article here.
Read more
 NASA brings standards of evidence to the search for UFOs
NASA brings standards of evidence to the search for UFOs
America’s space agency is convening a commission to investigate unidentified flying objects. In a Newsweek op-ed, Adam Frank explains why NASA’s involvement could be a game changer.
 Scientists hit key milestone in fusion energy quest
Scientists hit key milestone in fusion energy quest
The major breakthrough of achieving ignition is cause for celebration at Rochester’s Laboratory for Laser Energetics as well. “Now, we can see a future with a laboratory capability to both support the US nuclear deterrent and to start addressing the future for clean energy,” says LLE Director Chris Deeney.
 Are aliens real? Do aliens exist? Technosignatures may hold new clues
Are aliens real? Do aliens exist? Technosignatures may hold new clues
Adam Frank, professor of physics and astronomy, is searching for “technosignatures,” or the physical and chemical traces of advanced civilizations, among the 4,000 or so exoplanets scientists have found so far.
Category: Voices & Opinion