Hubble Views Face-On Barred Spiral Galaxy | Astronomy – Sci-News.com
The NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope has imaged a beautiful spiral galaxy called NGC 1022.
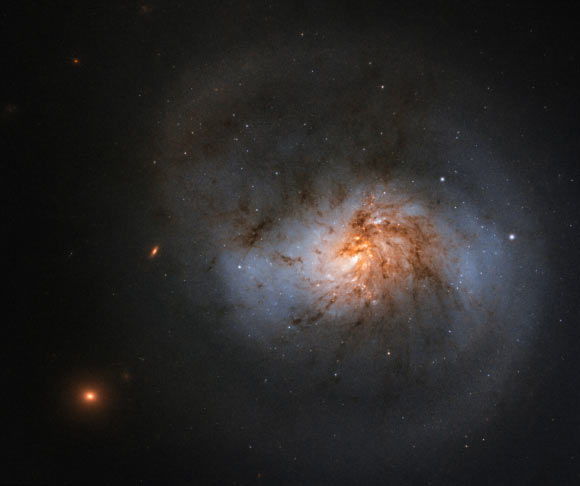

This Hubble image shows NGC 1022, a face-on barred spiral galaxy located in the constellation of Cetus, approximately 62 million light-years away. The image is made up of observations from Hubble’s Wide Field Camera 3 (WFC3) in the infrared and optical parts of the spectrum. Three filters were used to sample various wavelengths. The color results from assigning different hues to each monochromatic image associated with an individual filter. Image credit: NASA / ESA / Hubble / A. Seth.
NGC 1022 was discovered by the German-born British astronomer William Herschel on September 10, 1785.
The galaxy is located some 62 million light-years away in the constellation Cetus.
Also known as LEDA 10010 or IRAS 02360-0653, NGC 1022 is officially classified as a barred spiral galaxy.
“You can just about make out the bar of stars in the center of the galaxy in this Hubble image, with swirling arms emerging from its ends,” the Hubble astronomers said.
“This bar is much less prominent than in some of the galaxy’s barred cousins and gives the galaxy a rather squat appearance.”
“But the lanes of dust that swirl throughout its disk ensure it is no less beautiful.”
The astronomers observed NGC 1022 as part of a study into enormous black holes.
“They are fundamental components of galaxies, and are thought to lurk at the hearts of many — if not all — spirals,” the researchers said.
“In fact, they may have quite a large influence over their cosmic homes.”
“Studies suggest that the mass of the black hole sitting at a galaxy’s center is linked with the larger-scale properties of the galaxy itself.”
“However, in order to learn more, we need observational data of a wider and more diverse range of galaxies — something Hubble’s study aims to provide.”