9 of the Most Important Telescopes in the Universe of Astronomy – Interesting Engineering
The first optical telescope was created a little over . Though it is safe to assume that the technology found in telescopes has vastly improved, the mission is still the same. Astronomers and researchers alike use telescopes as their main tool to explore the universe, to peer into the great beyond, and to gain further insight into humanity’s place within it.
Coined by the Greek mathematician Giovanni Demisiani telescopes are optical instruments that make distant objects appear magnified by using an arrangement of lenses or curved mirrors and lenses, or various devices used to observe distant objects by their emission, absorption, or reflection of electromagnetic radiation.
SEE ALSO: SHOULD WE LOOK FOR ALIENS USING BLACK HOLE POWERED STARSHIPS
Across the planet, telescopes have been used to view distant stars and galaxies, as well as countless other celestial objects. Who knows, maybe a few aliens might have popped up on a few lenses.
Currently, there are seven classifications of telescopes that astronomers use, most of them is a big step from what you may have had laying in your bedroom as a kid. Each telescope uses a different method to scan the sky. There are x-ray telescopes, ultraviolet telescopes, optical telescopes, infrared telescopes, submillimeter telescopes, fresnel imagers, and finally x-ray optics.
Here is a little refresher crash course on everything you need to know about telescopes.
Now that you have got the basics down it is time to venture off and examine some of the most important telescopes in astronomy.
Galileo’s Telescope
Why not start where it all began? Though Galileo Galilei was not the inventor of the telescope or even the first person to point a spyglass up into the sky, he was one of the first astronomers to extrapolate what he saw in the night sky drawing conclusions about the universe that would forever change the way people viewed the night sky
His work would eventually earn him the title “ The Father of Modern Science”. Using his telescope, Galileo was busy observing the moon, discovering four of Jupiter’s moons, watching supernovas, and even verified the phases of Venus.
The Fermi Gamma-ray Telescope
As its name implies, The Fermi Gamma-ray Telescope uses gamma rays. A form of light, gamma rays are some of the most powerful forms of energy in the universe. Gamma-ray bursts tend to be created during the violent collision of stars or even in celestial events like black holes.
Hubble Space Telescope

Now, let’s move on to something that is more of a household name, the Hubble Telescope. Being in orbit for almost 30 years, the telescope takes its name from the famous American . Even if you have never heard about this telescope, you have for sure heard of some the Hubble’s tremendous accomplishments.
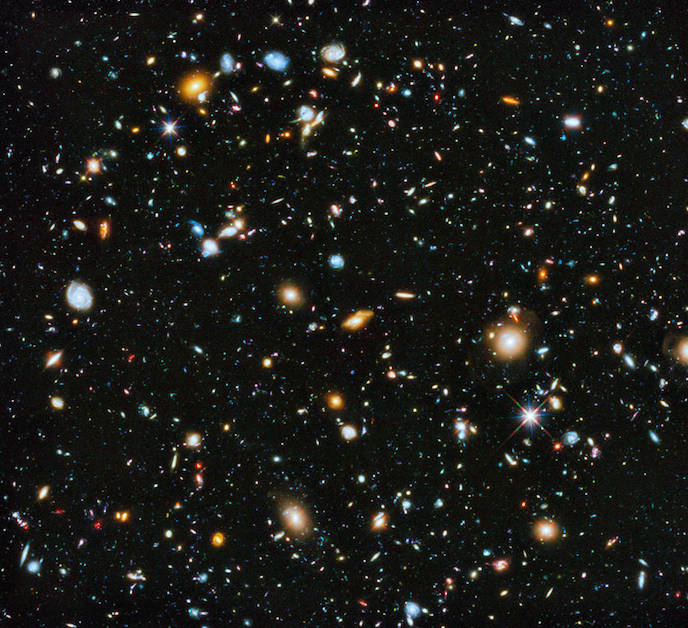

The Hubble Telescope has helped astronomers accurately estimate the age of the universe, gain further understanding of the planets in our solar system while taking shots at other exoplanets, and even snapping shots of other infant galaxies.
The MeerKAT Radio Telescope
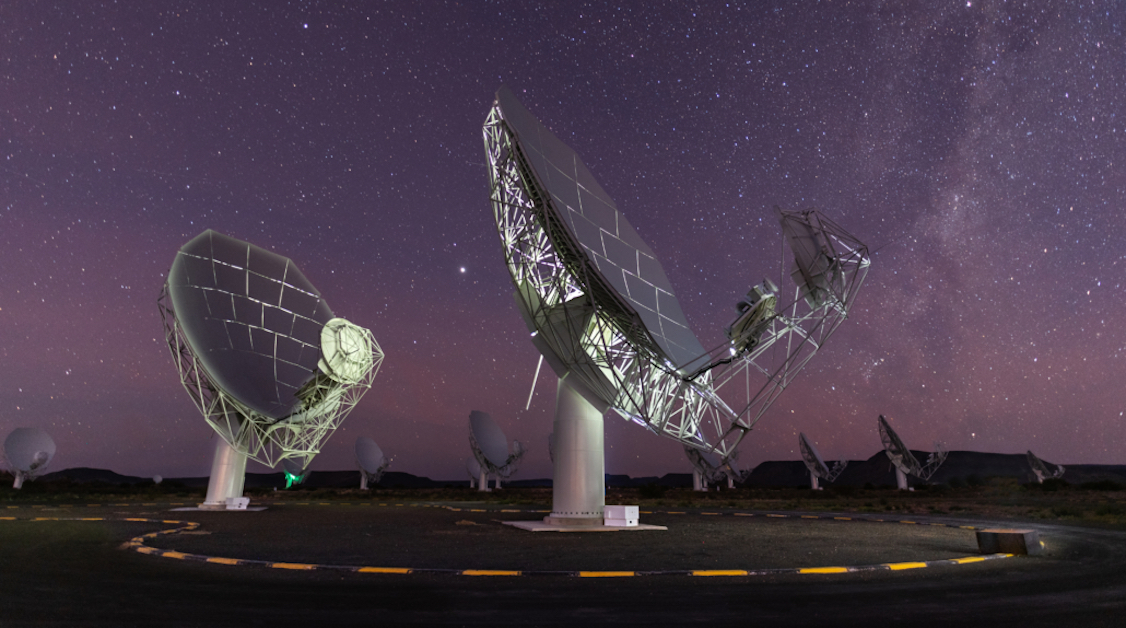

The force is strong with this one. Based in South Africa, the MeerKAT radio telescope has one of the more unique functions on this list. Comprising of , this telescope station will help astronomers gain further insight into dark matter and the gradual evolution of galaxies.
Already spotting more than , the MeerKAT is the largest and most sensitive radio telescope in the southern hemisphere.
Gemini Observatory
The Gemini Observatory is one of the more unique tools used by astronomers. Owned by seven different countries across the globe, the observatory is comprised of two identical with one on Hawaii’s Mauna Kea and another on central Chile’s Cerro Pachón; oceans apart.
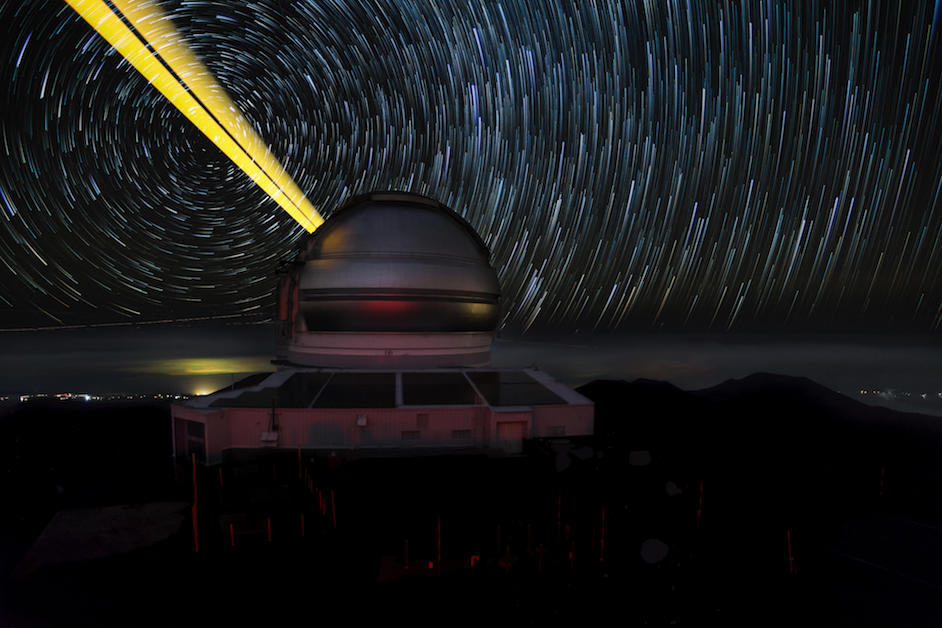

Gemini’s unique and advanced infrared capabilities, as well as its optical tech, allow it to probe into areas of the universe that would be otherwise impossible to see. The Gemini Observatory has observed everything from the birth of a supernova to a potentially habitable Earth-like planet.
The Spitzer Space Telescope
The Spitzer Space Telescope was launched in 2003 with the specific purpose of studying the early universe in infrared light. As one of the first telescopes to see light from a planet outside the solar system, Spitzer has made some impressive discoveries, finding fresh new comets, stars, exoplanets, and distant galaxies.
The Kepler Telescope
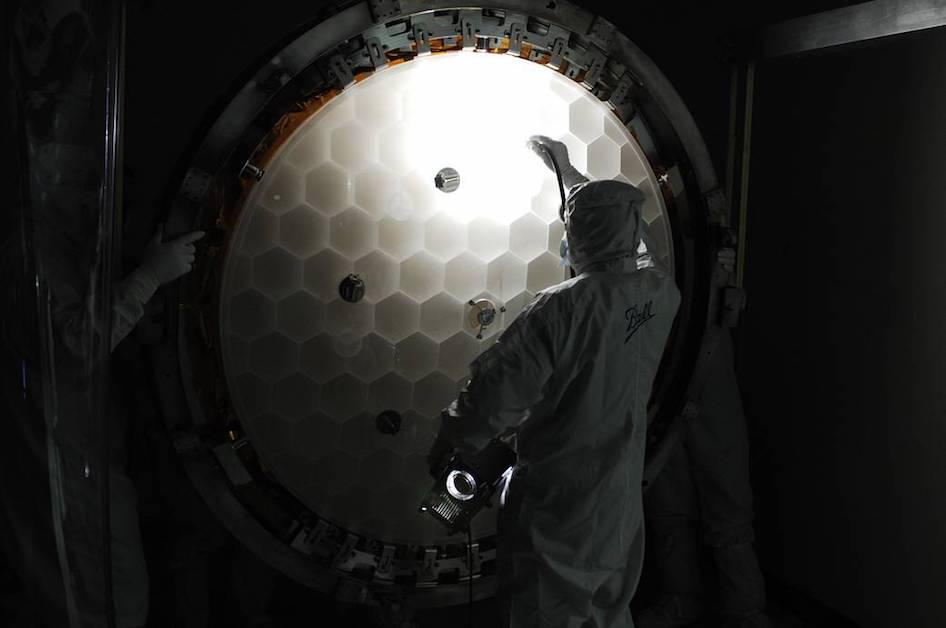

The planet hunter, the Kepler Telescope was created to scour the universe for any potential alien life and planets. Now officially in retirement, the telescope has discovered well over 2,600 planets outside our solar system during its nine-year career, making it one of the most successful telescopes ever.

The Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array
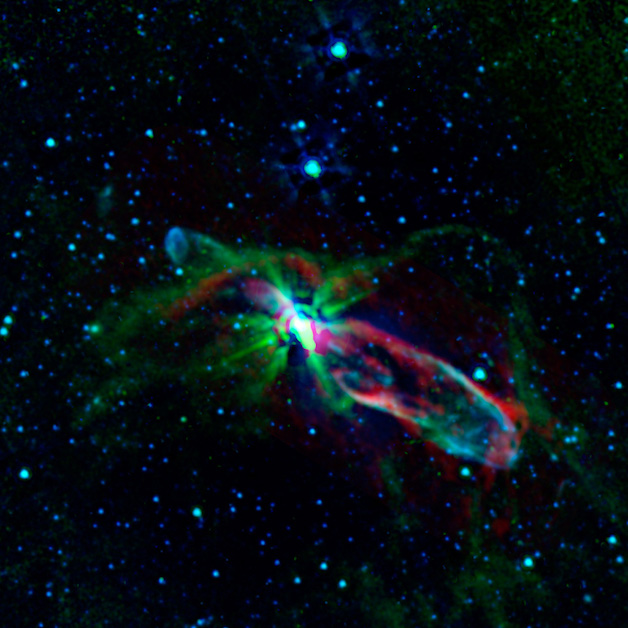

Spread across 10 miles and featuring in the Chilean Andes, these radio telescopes were once considered some of the most powerful and advanced on earth. Their discoveries laid the foundation for astronomer’s understanding of exoplanets.
The W.M. Keck Observatory
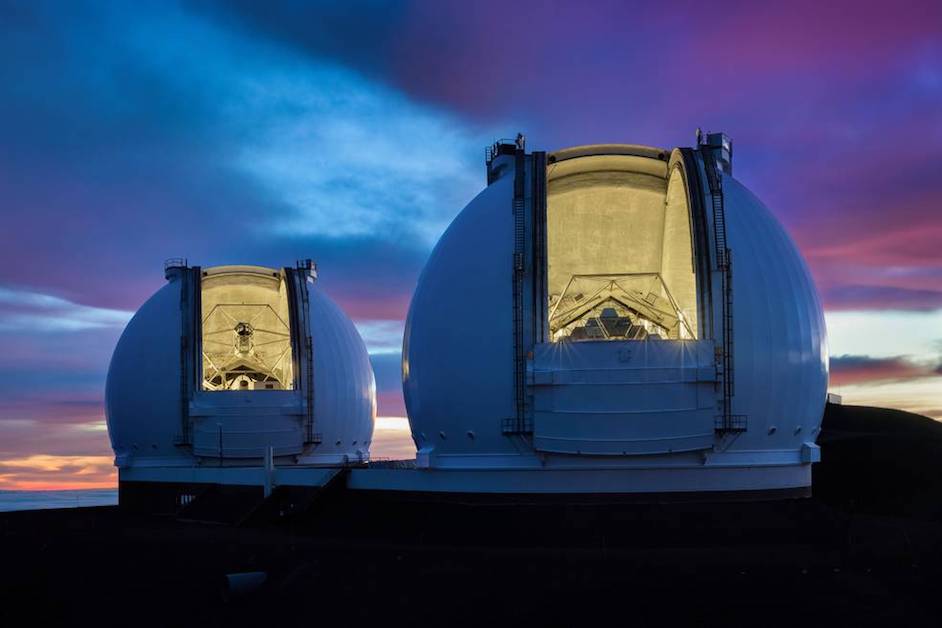

Located on the top of Mauna Kea, a dormant volcano in Hawaii, The W.M. Keck Observatory has been operating since 1993. Featuring two massive , the station offers the largest optical and infrared telescopes in the world.
The massive telescopes have proven to be fruitful churning out dozens of amazing discoveries. Each telescope has peered in the center of the Milky Way Galaxy, provided scientists more information on the Universe’s accelerated growth, and provided the first pictures of an exoplanet system, just to name a few.