Water Detected in Interstellar Comet 2I/Borisov | Astronomy – Sci-News.com
Astronomers have detected the signature of vaporized water in the coma of the interstellar comet 2I/Borisov, also known as C/2019 Q4.
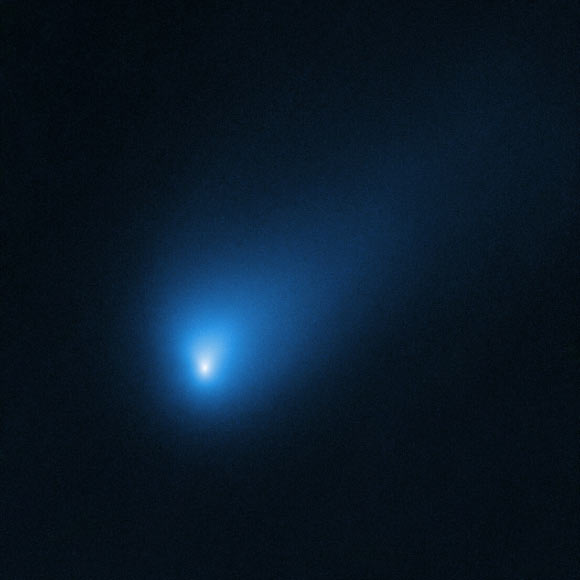

On October 12, 2019, Hubble observed the interstellar comet 2I/Borisov at a distance of approximately 261 million miles from Earth. Image credit: NASA / ESA / Hubble / D. Jewitt, University of California, Los Angeles.
Comets are thought to be repositories of primitive, unaltered matter left over from the birth of the Solar System.
This makes studies of cometary volatile materials powerful for understanding the physical and chemical processes occurring during planet formation.
“The discovery of the interstellar comet 2I/Borisov provides an opportunity to sample the volatile composition of a comet that is unambiguously from outside our own Solar System, providing constraints on the physics and chemistry of other protostellar disks,” said Dr. Adam McKay of NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center and American University and colleagues.
“As water (H2O) is the dominant volatile in most Solar System comets, measuring the H2O production in 2I/Borisov is key for interpretation of all other observations of this comet, including other volatiles.”
The astronomers analyzed spectra of 2I/Borisov obtained by the ARCES instrument, a high spectral resolution spectrograph mounted on the 3.5-m Astrophysical Research Consortium Telescope at Apache Point Observatory.
They detected the presence of water via the [O I] 6300 Å line emission.
“We determined an H2O production rate of 6.3*1026 mol/s,” the researchers explained, “which when compared to cyanide (CN) gas measurements suggest Borisov is either enhanced or typical in CN compared to the average value for Solar System comets, though the enhanced numbers are still within the range of observed values.”
“Diatomic carbon (C2), while likely depleted compared to CN, is either typical or depleted when compared to H2O.”
“Using a simple sublimation model, we found an H2O active area of 1.7 km2,” they added.
“More measurements are needed as 2I/Borisov approaches perihelion to fully understand its composition and activity.”
The findings will be published in the Astrophysical Journal Letters.
_____
Adam J. McKay et al. 2019. Detection of a Water Tracer in Interstellar Comet 2I/Borisov. ApJL, in press; arXiv: 1910.12785