How Technology Can Help Sports Advance After 2019 Rugby World Cup – Forbes

The 2019 Rugby World Cup has provided many key talking points
World Rugby via Getty Images
As the 2019 Rugby World Cup reaches its thrilling conclusion with England facing South Africa in Saturday’s final, it’s safe to say this year’s tournament has thrown up endless moments of brilliance – and plenty of talking points.
On the pitch, Japan thrilled in reaching the quarter-finals, while off it debate has raged over many controversial subjects.
Concussion fears, and the changes to tackling laws to allay them, have taken centre stage, while the challenging heat and humidity have seen a record number of handling errors committed.
As ever, the solution to these problems most likely lies in technology.
CONCUSSIONS
While concussion is rightly a key issue within rugby and many steps have been taken to improve player safety over recent seasons, it remains a difficult injury to truly quantify.
Head Injury Assessment protocols, used to assess players off the pitch immediately after a collision, have proved effective so far, but they still provide only a small insight into the injury.
A longer-term solution may be found in an unusual place.
OPRO
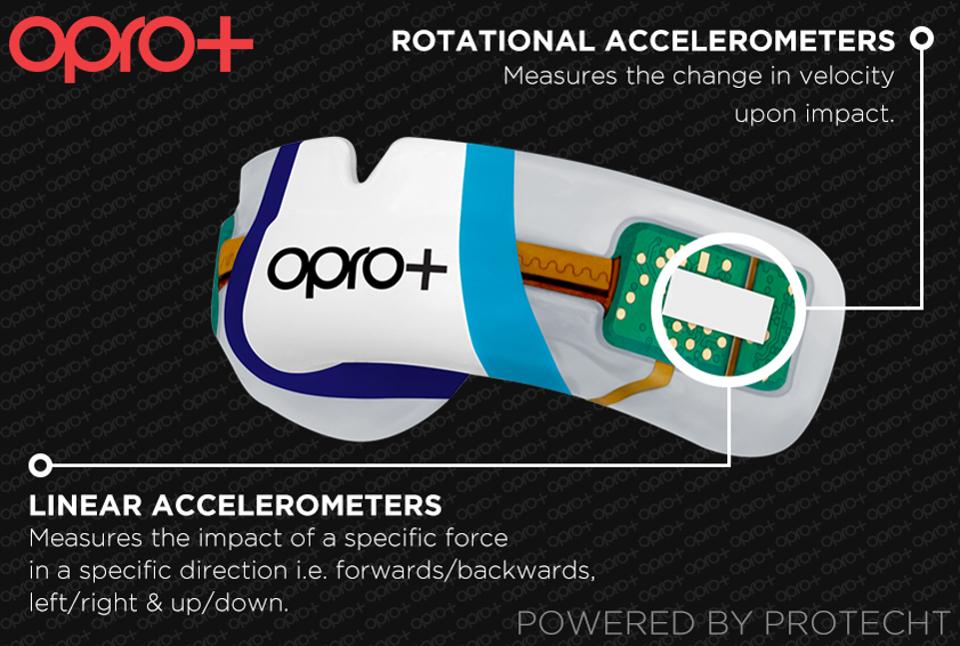
World-leading mouthguard manufacturer OPRO have been working with electronics firm SWA on a device fitted with circuit boards designed to measure head impacts.
The hope is that, with time, the mouthguard can be used to measure the force of impact from pitchside and provide real-time feedback to a pitchside team.
Dr Anthony Lovatt, of OPRO, says: “The mouth is perfect for gathering data from sensors. Anywhere else you place a sensor there is some underlying movement. If you place it on the neck or the head the skin moves and you get wildly incorrect data.
“It is firmly attached to the teeth, the jawbone, and the skull. The strong correlation between the data picked up by a mouthguard and what is happening in the skull of a player.”
OPRO
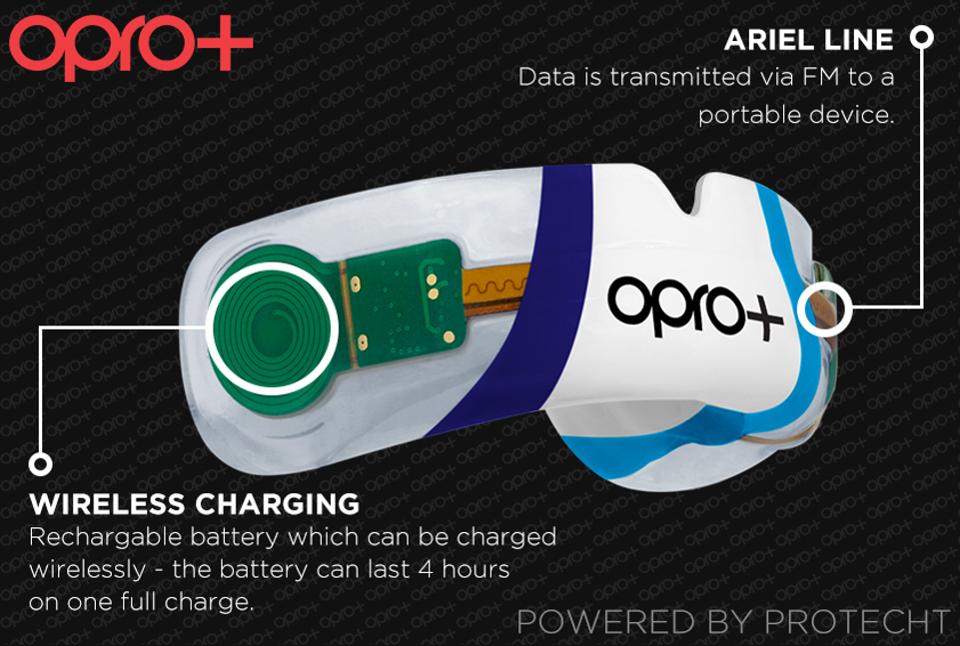
Dr Lovatt admitted there are difficulties in ensuring the complexities of electronics are fit to be placed in a mouth, but that such is the advance of the technology it could be available for grassroots rugby clubs swiftly – but there is still more work to do.
He says: “The obstacles is making sure everything is compliant. As it happened, its not too much of an obstacle. One of the beauties of the SWA system is there is nothing in the front of the mouth except a wafer thin aerial.
“The SWA system is really neat in how it fits in the mouth. It has gone through all the compliance tests, and what you end up with is a fully-approved mouthguard.
“Hopefully in four or five years time that data can provide more definitive answer once people have worked out the constituent parts for a concussion to happen.”
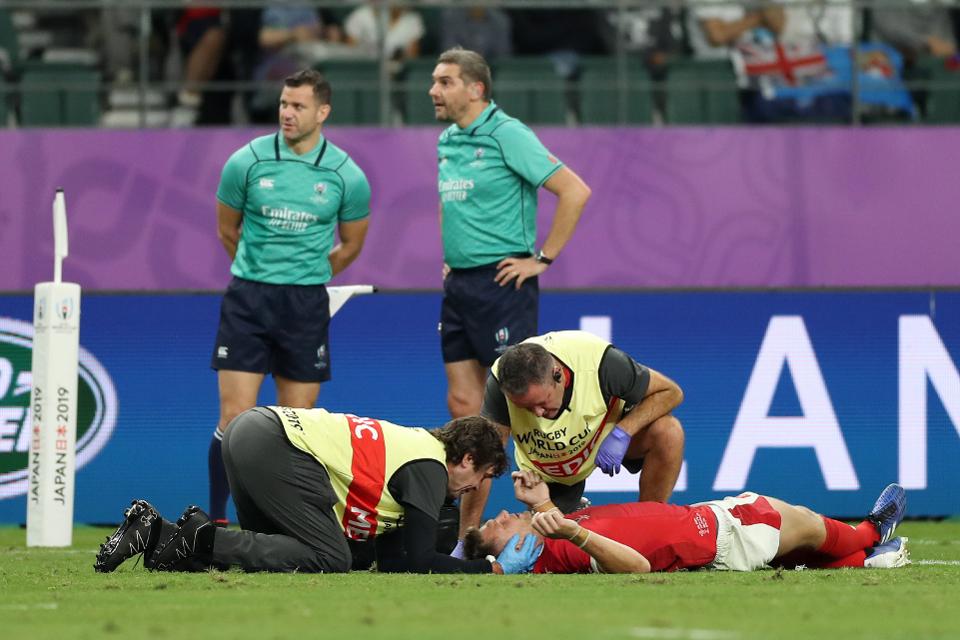

Wales fly-half Dan Biggar recieves treatment after a head injury
Getty Images
ADAPTING TO CONDITIONS
There have been undoubted positives in taking the Rugby World Cup to Asia for the first time; huge crowds, unforgettable atmospheres and thrilling matches have justified the decision.
However, beyond Typhoon Hagibis, which led to three matches being cancelled, the games have been played in incredibly humid conditions.
That has made executing basic skills very tricky, with England racking up a huge 41 handling errors in one game against U.S.A in the pool stage.
Again, solutions have been found ensuring kit and equipment is suitable for conditions.
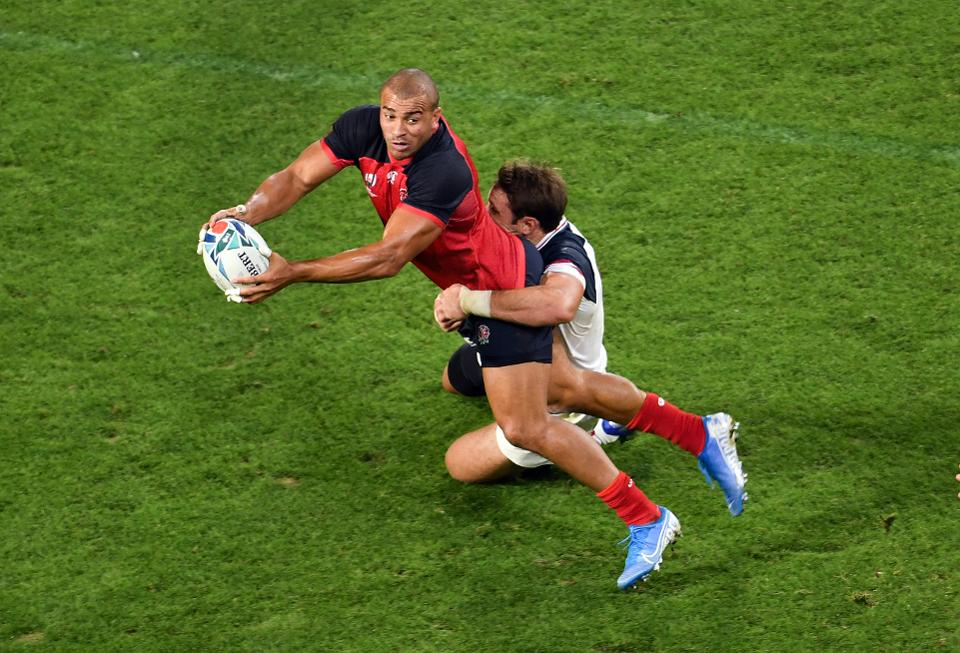

A number of handling errors were made by England against U.S.A
Getty Images
Charlotte Cox, brand director at Canterbury says: “The teams have faced many unique challenges in Japan, including a change in culture and climate, as well as the travelling between a variety of locations across the different islands.
“This will be exciting and new – but possibly unfamiliar to the players. It is important to cater for each possible occasion and variability in weather by providing a wide range of clothing to give the players and the coaching teams the necessary choice and comfort.”
As well as combating conditions, the kits can also have performance benefits; the skin-tight fit, makes it trickier for opponents to grip the shirt.
Already, thoughts are turning to the 2023 Rugby World Cup, to be held in the more familiar environment of France. Still, that hasn’t stopped kit manufacturers seeking to innovate.
Cox adds: “Quite simply we cycle back to the first phase of the research process. A brief has already been developed for the Rugby World Cup 2023, so the innovation team are about to begin work on the next version of match kit.”
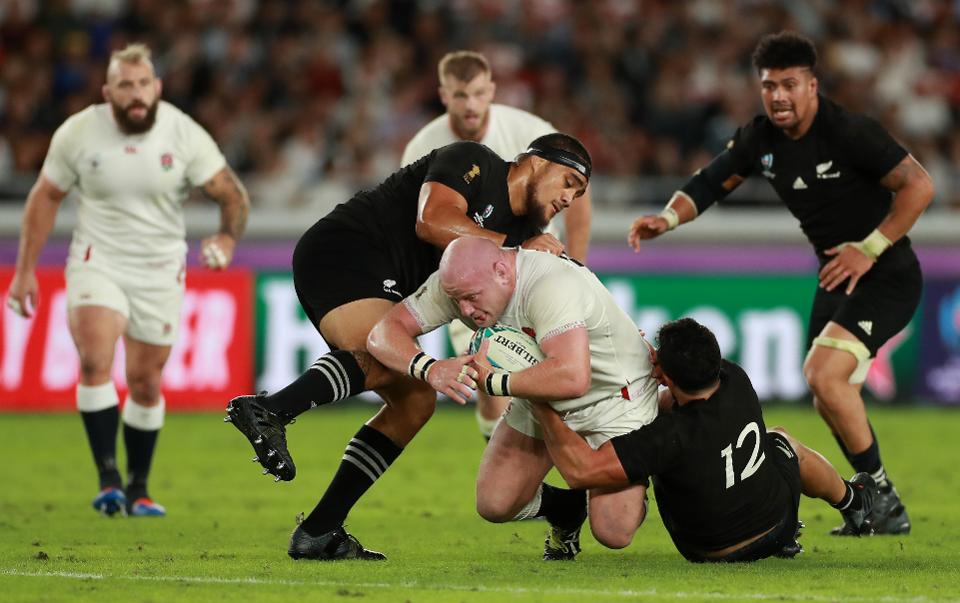

England are using advanced technology in their shirts to enhance performance
Getty Images
WEARABLE TECHNOLOGY
Gathering data from wearable technology in both training and games is now a given for any top-level sports teams.
The real question is where it goes from here, both at a professional and amateur level.
The finalists, England and South Africa, are two of 12 teams at the tournament using technology from STATSports to track player performance and development.
Sean O’Connor, founder of STATSports, says: “People get fixated on more data, and the term big data, I’m not a huge fan of it. We have to get smarter with it.
“With elite sports team, you have a small window to get data, download it, analyse it and get reports done.
“If you add bucket loads of data to that, something has to give.”
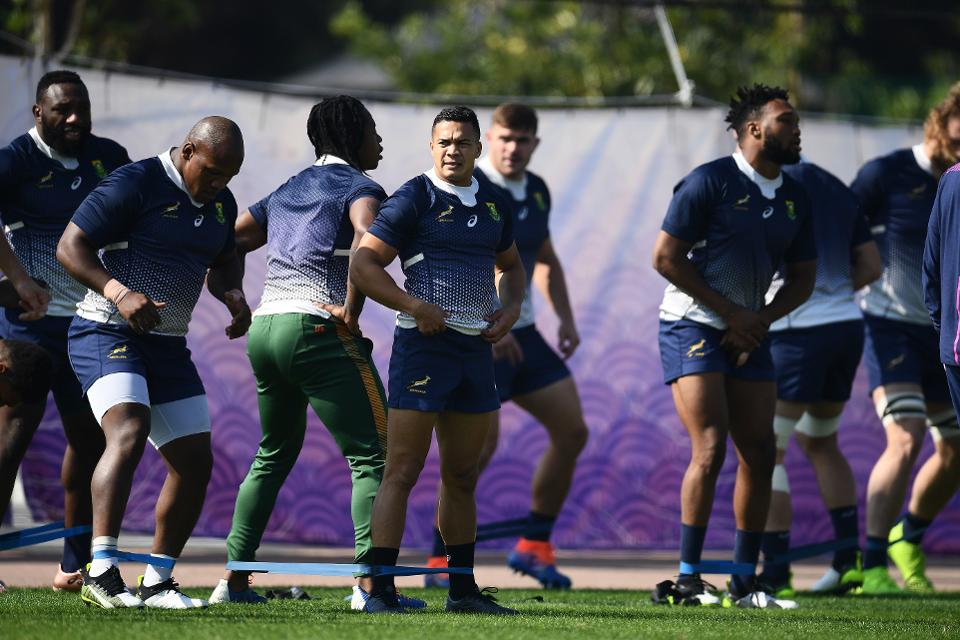

Finalists South Africa use STATSports equipment to measure performance
AFP via Getty Images
For an idea of what comes next, STATSports are one of several technology companies working on developing shorts that would relay information on a player’s muscle tension, hamstrings and balance.
However, O’Connor believes that technology also has the ability to open up brand new commercial opportunities to.
He says: “In broadcast and in fan engagement is where we really see this going. It is a whole new level of engagement with fans, who can not only wear the boots their superstars wear, but wear the same technology as them too.
“If you go back 10-15 years, not too many people were wearing garments when running or doing triathlon but now it is ubiquitous, it is now only a matter of time before it reaches team sports.
“Data is everywhere you look. Kids playing games and consuming data without even knowing it. We think the world is becoming more and more ready for that.”
OFFSIDES
Such was the concern over adjudicating offside calls, that World Rugby deputy chairman Agustin Pichot revealed mid-tournament that Hawk-Eye technology could be introduced in the near future.
The group stage in particular was marred by difficulties in policing the offside line, with Louis Picamoles snaffling an offside interception in Wales’ 23-21 win over Argentina.
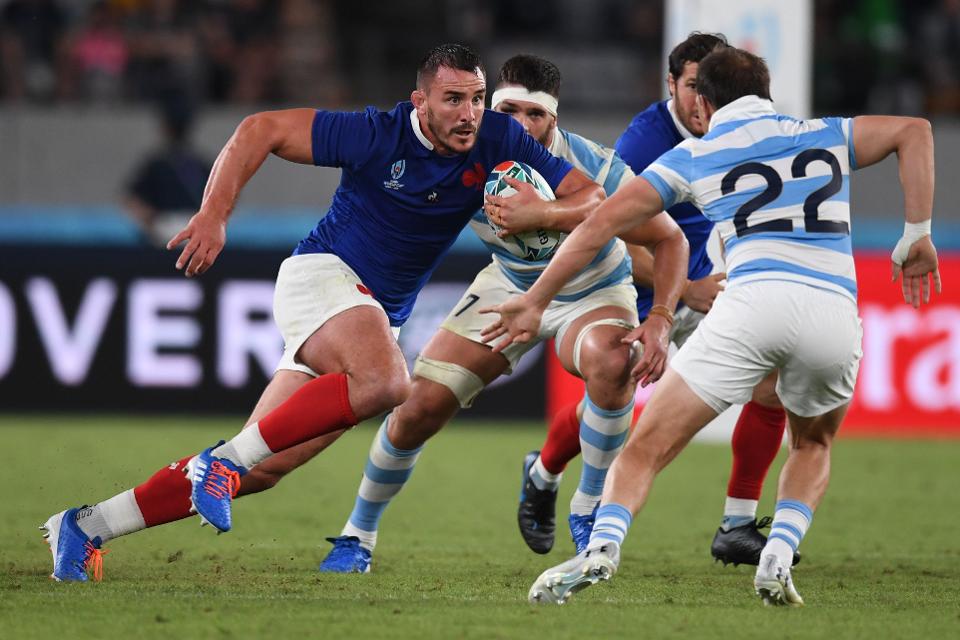

France’s back row Louis Picamoles made an interception from an offside position against Argentina
AFP/Getty Images
Most prominently used at Wimbledon to judge line calls, the equipment could be adapted from tennis to rugby and give the referees a new set of eyes on the field.
World Rugby vice-chairman Agustin Pichot previously told Daily Mail Sport: “Technology which provides straight lines for the TMO, that is one of our ideas.
“Hawk-Eye could tell the touch judges immediately whether the defenders are offside. You put two lines on the end of the ruck, on the back foot, which feeds back to the officials.”