Hubble Snaps Stunning Image of Spiral Galaxy NGC 3749 | Astronomy – Sci-News.com
The NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope has captured an amazing new photo of a galaxy called NGC 3749.
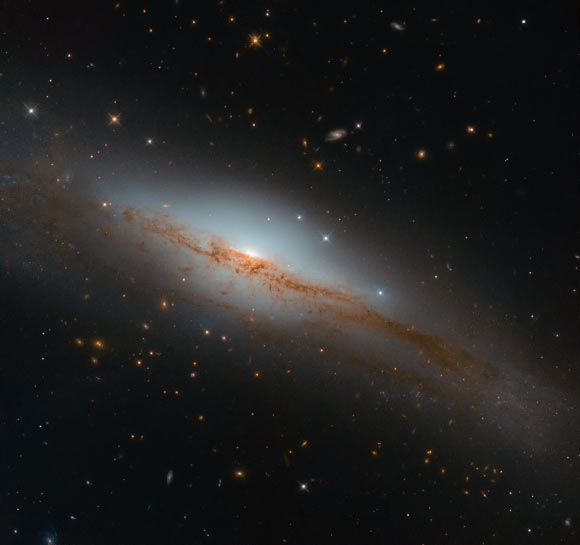

This new image from the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope shows the spiral galaxy NGC 3749. The image is made up of observations from Hubble’s Wide Field Camera 3 (WFC3) in the infrared and optical parts of the spectrum. Two filters were used to sample various wavelengths. The color results from assigning different hues to each monochromatic image associated with an individual filter. Image credit: NASA / ESA / Hubble / D. Rosario et al.
NGC 3749 is a spiral galaxy located 118 million light-years away in the constellation Centaurus.
The galaxy was discovered on April 21, 1835 by the English astronomer John Herschel.
Otherwise known as LEDA 35861 and ESO 320-8, it is classified as an emission-line galaxy.
NGC 3749 has been used a ‘control’ in studies of especially active and luminous galaxies — those with centers known as active galactic nuclei.
In comparison to its active cousins, the galaxy is inactive and has no known signs of nuclear activity.
“When we explore the contents and constituent parts of a galaxy somewhere in the Universe, they use various techniques and tools,” the Hubble astronomers explained.
“One of these is to spread out the incoming light from that galaxy into a spectrum and explore its properties. This is done in much the same way as a glass prism spreads white light into its constituent wavelengths to create a rainbow.”
“By hunting for specific signs of emission from various elements within a galaxy’s spectrum of light (emission lines) or, conversely, the signs of absorption from other elements (absorption lines), we can start to deduce what might be happening within,” they said.
“If a galaxy’s spectrum shows many absorption lines and few emission lines, this suggests that its star-forming material has been depleted and that its stars are mainly old, while the opposite suggests it might be bursting with star formation and energetic stellar newborns.”
“This technique known as spectroscopy, can tell us about a galaxy’s type and composition, the density and temperature of any emitting gas, the star formation rate, or how massive the galaxy’s central black hole might be.”
“While not all galaxies display strong emission lines, NGC 3749 does!”